What is pulmonary fibrosis?
Pulmonary - LUNG
Fibrosis - SCARRING
Idiopathic PF (IPF) refers to PF that develops because of an unknown cause.
How does it affect the lungs?
- Thickening of the lower parts of the lung (alveoli)
- The lungs stiffen as a result of tissue scarring, making deep breathing more difficult
- Scar tissue reduces the amount of oxygen that leaves the lungs and enters the bloodstream
- Lung size and capacity is reduced
Symptoms

Progressive difficulty in breathing

Tiredness

Persistently dry or mildly mucus productive cough

Loss of appetite and weight
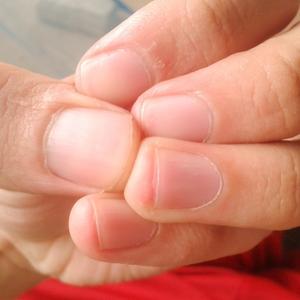
Rounded and swollen fingertips (clubbing)
What are the risk factors of developing pulmonary fibrosis?
Whilst some people are genetically at an increased risk of developing PF, there are also environmental risk factors that can impact the development of PF such as breathing in smoke or dust.
Biological factors

Genetics
- Some genes have been identified to increase the risk of developing PF
- There is currently no testing available to determine who may be susceptible to developing PF

Age
- Some genes have been identified to increase the risk of developing PF
- There is currently no testing available to determine who may be susceptible to developing PF
Viral infections
- Exacerbations of PF can be triggered by viruses, other infections or trauma/surgery

Gastroesophageal Reflux
- The spill over of stomach chemicals into the lungs may lead to scarring
- Elevating the head of your bed may reduce reflux

Autoimmune Disease
- The immune system attacks it's own cells in autoimmune disease
- Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and scleroderma are commonly associated with PF
- RA causes inflammation of the joints

Sex
- Men are more commonly affected by PF than women
Environmental factors

Smoking
- Brings in inflammatory cells to the lungs from the blood
- Leads to inflammation and damages lung tissue

Medication
- Cancer treatment such as radiotherapy and chemotherapy can cause damage to the lung tissue
- Some medication and drugs have been associated with PF disease

Industial exposure
- Irritation of the lungs and increased tissue scarring can be caused by asbestos, organic dust from agriculture, metal and wood
Content acknowledgements: © 2022 by the University of Hull and Authors. A Patient's Guide to Pulmonary Fibrosis Second Edition